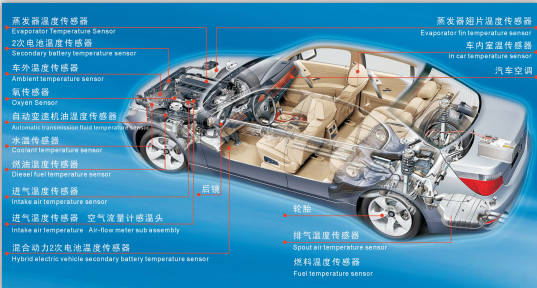
The temperature sensors on the car are mostly negative temperature coefficient thermistors, such as the engine intake temperature sensor, coolant temperature sensor, oil temperature sensor, automatic transmission and oil temperature sensor of the continuously variable transmission, the dual clutch transmission is responsible for monitoring the transmission oil bottom. G93 transmission oil temperature sensor with shell oil temperature, G509 temperature sensor for monitoring the working oil temperature of the transmission clutch, indoor temperature sensor for air conditioner, ambient temperature sensor, evaporator temperature sensor, suspension air pump temperature sensor, etc. are all negative temperature coefficient heat Sensitive resistance. It is characterized by the higher the temperature of the measuring point, the lower the resistance value of the sensor, and the lower the output voltage signal. Taking the Mazda intake air temperature sensor as an example, when the ambient temperature is -20 ° C, 20 ° C, and 60 ° C, the resistance values are 13.6 to 18.4 kΩ, 2.21 to 2.69 kΩ, and 0.493 to 0.6967 kΩ, respectively.
The common fault of the negative temperature coefficient thermistor sensor is that the signal is abnormal, the sensor or harness is short-circuited, the data stream will have a false high temperature signal; the sensor or harness disconnection, the terminal water inlet or the grounding wire will be in poor contact, and the data flow will have a false low temperature. signal. In addition, the control unit A/D converter is converted incorrectly, and a false high temperature signal may appear in the data stream.
First, the intake air temperature sensor
1.Intake air temperature sensor function
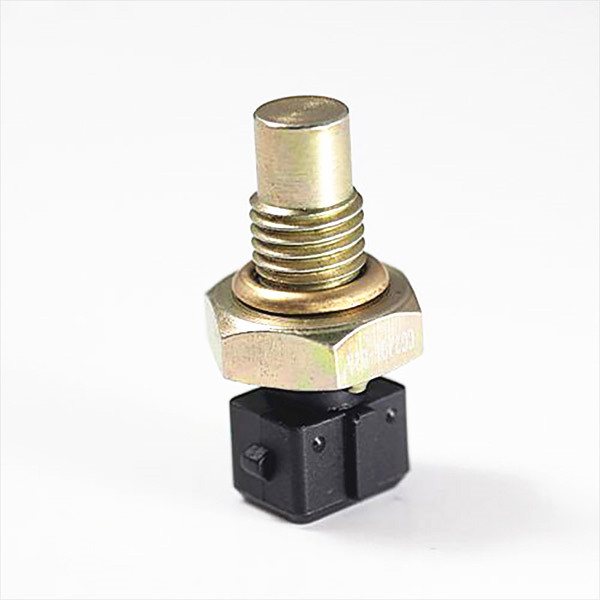
Except for the Karman vortex air flow sensor, the other engines are equipped with an intake air temperature sensor, as shown in Figure 1. The intake air temperature sensor can be installed in the air flow sensor or the intake pressure sensor, or it can be installed in a certain part of the intake port. When the engine intake temperature is high, the control unit will reduce the injection pulse width, and vice versa.
2.Intake air temperature sensor failure analysis
The intake air temperature sensor has poor contact with the ground wire, the data flow will show abnormally low temperature, and the low temperature air density will increase the injection pulse width, causing the mixed steam to be too rich. If the sensor is short-circuited, the data flow will show abnormally high temperature, and the high-temperature air density will be low, which will reduce the fuel injection pulse width and cause the mixed steam to be too thin. Intake air temperature sensor temperature is higher the more concentrated vapor mixture, a sensor circuit or poor grounding can cause vapor lean mixture, resulting in difficulty in starting.
Second, the coolant temperature sensor
1.The role of the coolant temperature sensor
The coolant temperature sensor terminal is 2 pins, one is the input signal line and the other is the output signal line; the terminal is 4 pins, then the 4 pins are the input signal line, the output signal line, the control unit ground wire and the instrument panel. Ground wire, as shown in Figure 2. The coolant temperature sensor is usually installed at the rear thermostat or radiator outlet of the engine, and is responsible for the injection pulse width, warm-up, ignition advance angle, automatic transmission torque converter lock and over-speed control, and air-conditioning control. The main functions are:
1 is responsible for controlling the concentration of the mixed vapor. The lower the temperature, the thicker the mixed vapor; the higher the temperature, the thinner the mixed vapor.
2 is responsible for controlling the engine speed when warming up, the speed below 40 °C is 1500r/min, and the speed of 40~70°C is 1100r/min.
3Responsible for controlling the radiator fan, starting at low speed above 85 °C, starting at high speed at 105 °C.
4 is responsible for controlling the automatic transmission, the torque converter above 56 °C enters the locking condition, and the 70 °C transmission is allowed to enter the overspeed.
5 is responsible for controlling the air conditioner, 120 °C air conditioning exit control.
2.Coolant temperature sensor failure analysis
The engine coolant temperature sensor is short-circuited, the data flow will show a high temperature above 100 °C, causing the mixed steam to be too thin to start; the sensor is broken or the ground wire is not in good contact, and the data flow will show a low temperature below -30 °C, causing the mixture to be too rich. The exhaust pipe emits black smoke.
The OBD-I system sets the engine control unit to define the coolant temperature sensor sensing temperature between -35 and 120 °C. If it exceeds or falls below this range, the control unit can determine that the sensor is faulty and will not be within this range. A trouble code appears. If the coolant temperature sensor is short-circuited, the data flow indicates that the coolant temperature exceeds 100 °C when the ignition switch is turned on, but since it does not reach 120 °C, the fault code is not left.
The monitoring of the combined electrical appliances by the OBD-II system mainly compares the information of the sensors that provide relevant information or common information, in order to determine which particular sensor is faulty, whether it is a short circuit or an open circuit. If the information of the coolant temperature sensor is compared with the information of the intake air temperature sensor or the time after starting, it can be determined whether the information of the coolant temperature sensor is accurate, whether the sensor has a short circuit or an open circuit fault. Therefore, the OBD-II system will leave a fault code after the coolant temperature sensor is short-circuited.
Third, the transmission oil temperature sensor
The automatic transmission oil temperature sensor is mounted on the control valve, and the transmission is mainly subjected to high temperature control, as shown in Figure 3.
When the transmission oil temperature is higher than 150 °C, the torque converter immediately enters the locking condition. If the transmission oil temperature does not decrease after 30s, the torque converter is unlocked and the transmission exits the overspeed. The oil temperature sensor itself or the wire harness is short-circuited, and the data flow will show that the transmission oil temperature is higher than 150 ° C. Therefore, after the oil temperature sensor itself or the wire harness is short-circuited, the torque converter does not enter the locking condition, the transmission has no over-speed gear, and the car has no high speed.
Taking the oil temperature sensor of the Magotan dual clutch transmission as an example, the transmission oil temperature sensor is G509 and G93, wherein G93 is responsible for monitoring the transmission oil sump oil temperature, ie the transmission oil temperature; G509 (Fig. 4) is responsible for monitoring the clutch working oil temperature in the transmission. The flow of the clutch cooling oil is adjusted according to the change of the oil temperature, and other corresponding measures are taken to protect the transmission. If one of the dual clutches slips and the oil temperature of the electro-hydraulic control unit exceeds 138 °C, the transmission control unit enters the overload protection, reduces the engine output torque, calculates the amount of the clutch working oil temperature exceeding the rated value, and reduces the engine torque. As small as the idle limit, the clutch overload is almost non-existent, achieving the purpose of cooling the clutch cooling system. The engine then re-supplies the maximum torque, the clutch oil temperature exceeds 145 ° C (the clutch is severely slipping), the supply of oil to the clutch is stopped, and the two clutches are in the open position. The G509 of the oil temperature at the clutch oil outlet will give the transmission control unit a high temperature signal, the control unit will enter the overload protection, and there is only one failure protection gear in the D position. The dual clutch should be replaced immediately (the two clutches must be replaced in pairs).
If the G509 is short-circuited, the data flow will show that the clutch oil temperature exceeds 150 °C, the transmission control unit enters the overload protection, and there is only one second gear in the D position.
Fourth, the temperature sensor on the air compressor
The air suspension is equipped with a temperature sensor on the nitrogen air compressor. When the compressor temperature reaches 130 °C, the compressor is temporarily interrupted to prevent ablation from occurring at a high temperature. Once the air pump is ablated, the height of the car always stays at the lowest position and no longer rises.
Fivth, air conditioning temperature sensor
Automatic air conditioning system temperature sensors include:
Engine coolant temperature sensor, interior temperature sensor, ambient temperature sensor, evaporator temperature sensor, solar radiation sensor, refrigerant temperature control switch, etc. Based on these sensor signals, the control unit calculates the temperature required to blow the air into the cabin, selects the required amount of air, and then controls the air mixing inlet, the water valve, the inlet and outlet port conversion plates, etc., within the temperature range set by the driver. Automatically adjusts the temperature inside the cabin to optimize it and automatically controls the opening and closing of the air conditioner.
To protect the engine when the engine coolant temperature exceeds 120 ° C, the air conditioner will stop working. The temperature of the refrigerant in the air conditioner compressor is too high, and the temperature switch will cut off the circuit of the electromagnetic clutch of the compressor. An evaporator temperature sensor or temperature switch installed in the center of the evaporator controls the temperature of the evaporator by controlling the operation of the air conditioner compressor. The purpose of the evaporator temperature control is to prevent frosting of the evaporator. If the temperature of the evaporator is lower than 0 °C, the moisture condensed on the surface of the evaporator will be frosted or frozen, and in severe cases, the air passage of the evaporator will be blocked, resulting in a significant reduction in the cooling effect of the cooling system. In order to avoid frosting of the evaporator, the temperature of the evaporator must be controlled above 0 °C. When the evaporator temperature is too low, below the set value below 0 °C, the air conditioner amplifier will cut off the circuit of the compressor electromagnetic clutch. Failure of the evaporator outlet temperature sensor can cause the air conditioner compressor clutch to be frequently engaged and disengaged. Frosting in the pipe between the expansion valve and the evaporator will result in a small amount of airflow from the air conditioner.
One of the conditions for air conditioning system cooling is that the ambient temperature is higher than the indoor temperature, the ambient temperature sensor is open, the terminal is in the water, the contact is poor, or the grounding is poor. The data flow will indicate that the ambient temperature is below -30 °C, which will cause the air conditioner to not cool.
At the same time, the engine coolant temperature sensor is disconnected or the grounding wire is in poor contact. When the signal is out of alignment, the cooling fan does not turn, resulting in poor heat dissipation of the air conditioner, and also enters the fail-safe protection to stop the air conditioner.
Sixth, typical case analysis
1.Fault phenomenon
In an Audi A8 sedan, the air pump of the electronically controlled suspension often withdrew from control, which made it impossible for the car to change the height and hardness of the vehicle according to changes in road conditions and driving conditions, so it went to a repair shop for repair. After the repair, the air pump is no longer out of control, but after a period of use, the height of the car always stays at the lowest position and no longer rises. There is no fault code.
2.Fault diagnosis and analysis
The height of the car always stays at the lowest position and no longer rises, indicating that the air pump is no longer working. The reasons why the air pump does not work are:
1 The temperature sensor on the air pump is short-circuited, the data flow will show that the air pump temperature exceeds 130 °C, the control unit will make it out of control; 2 The suspension control unit A / D converter is converted incorrectly, the data flow will show that the air pump temperature exceeds 130 °C, the control unit will exit the control; 3 After the air sensor on the air pump fails to exit, the control unit enters the fail-safe, sets a assumed temperature value, and the air pump is no longer subject to temperature control. When the car is running on a bad road, the air pump continuously works, which may cause high temperature ablation.
After inspection, it was found that the control unit entered the fail-safe protection due to the artificial disconnection of the temperature sensor terminal on the air pump, causing the air pump to ablate at a high temperature. Why disconnect the sensor terminals? The original body control unit A/D converter was incorrectly converted, resulting in the air suspension often remaining at the lowest position. The maintenance personnel detected that the temperature sensor on the air pump was normal. Since the cause of the failure was not found, the temperature sensor terminal on the air pump was manually disconnected, and the suspension could be self-adjusted, resulting in high temperature ablation of the air pump.
Troubleshoot after replacing the air pump and body control unit.